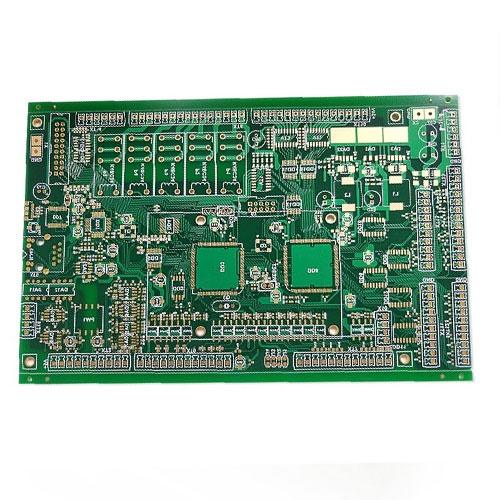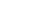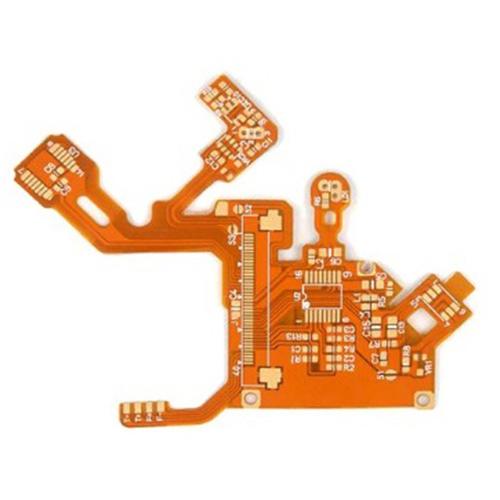
Multilayer PCB Circuit Board
Double Sided PCB is the middle layer of medium, and both sides are wiring layers. Multilayer PCB is a multi-layer wiring layer. Between every two layers is a dielectric layer. The dielectric layer can be made very thin. Multilayer PCB has at least three conductive layers, two of which are on the outer surface, and the remaining layer is integrated into the insulating board. The electrical connection between them is usually achieved through plated through holes on the cross section of the circuit board.
The distinction of Multilayer PCB
The circuit board determines the process difficulty and processing price according to the number of wiring surfaces. Common circuit boards are divided into single-sided wiring and double-sided wiring, commonly known as Double Sided PCB and Double Sided PCB. However, high-end electronic products are restricted by product space design factors. In addition to surface wiring, multiple layers of circuits can be superimposed inside. During the production process, after each layer of wiring is made, it is positioned and pressed by optical equipment to superimpose the multilayer circuits on a circuit board. Commonly known as Multilayer PCB. Any circuit board with more than or equal to 2 layers can be called Multilayer PCB. Multilayer PCB can be divided into Multilayer Rigid PCB, Multilayer Flexible PCB, Multilayer Rigid-flex PCB.
The birth of Multilayer PCB
The increase in the packaging density of integrated circuits has resulted in a high concentration of interconnect lines, which necessitates the use of Multilayer PCB. In the layout of the printed circuit, unforeseen design problems such as noise, stray capacitance, and crosstalk have appeared. Therefore, the printed circuit board design must focus on minimizing the length of signal lines and avoiding parallel routes. Obviously, in Single Sided PCB, even Double Sided PCB, due to the limited number of crosses that can be achieved, these requirements cannot be answered satisfactorily. In the case of a large number of interconnection and crossover requirements, to achieve a satisfactory performance of the circuit board, the board layer must be expanded to more than two layers, thus the Multilayer PCB appeared. Therefore, the original intention of manufacturing Multilayer PCB is to provide more freedom in choosing suitable wiring paths for complex and/or noise-sensitive electronic circuits. Multilayer PCB has at least three conductive layers, two of which are on the outer surface, and the remaining layer is integrated into the insulating board. The electrical connection between them is usually achieved through plated through holes on the cross section of the circuit board. Unless otherwise specified, Multilayer PCB, like Double Sided PCB, is generally plated with through-holes.
Multilayer PCB is made by stacking two or more circuits on top of each other, with reliable pre-set interconnections between them. Since drilling and plating have been completed before all the layers are rolled together, this technique violates the traditional manufacturing process from the beginning. The two innermost layers are composed of traditional double panels, while the outer layers are different, they are composed of independent single panels. Before rolling, the inner substrate will be drilled, through-hole plating, pattern transfer, development and etching. The outer layer to be drilled is the signal layer, which is plated through in such a way that a balanced copper ring is formed on the inner edge of the through hole. The layers are then rolled together to form a Multilayer PCB, which can be connected to each other (between components) using wave soldering.
Rolling may be done in a hydraulic press or in an overpressure chamber (autoclave). In the hydraulic press, the prepared material (for pressure stacking) is placed under cold or preheated pressure (the material with high glass transition temperature is placed at a temperature of 170-180°C). The glass transition temperature is the temperature at which an amorphous polymer (resin) or part of the amorphous region of a crystalline polymer changes from a hard, rather brittle state to a viscous, rubbery state.
Multilayer PCB is put into use in professional electronic equipment (computers, military equipment), especially when the weight and volume are overloaded. However, this can only be achieved by increasing the cost of Multilayer PCB in exchange for an increase in space and a reduction in weight. In high-speed circuits, Multilayer PCBs are also very useful. They can provide designers of printed circuit boards with more than two layers of board to lay wires and provide large grounding and power supply areas.