Surface mount soldering joint formation process and metallographic organization
date:Apr 19,2019
Return listSurface mount soldering joint formation process and metallographic organization
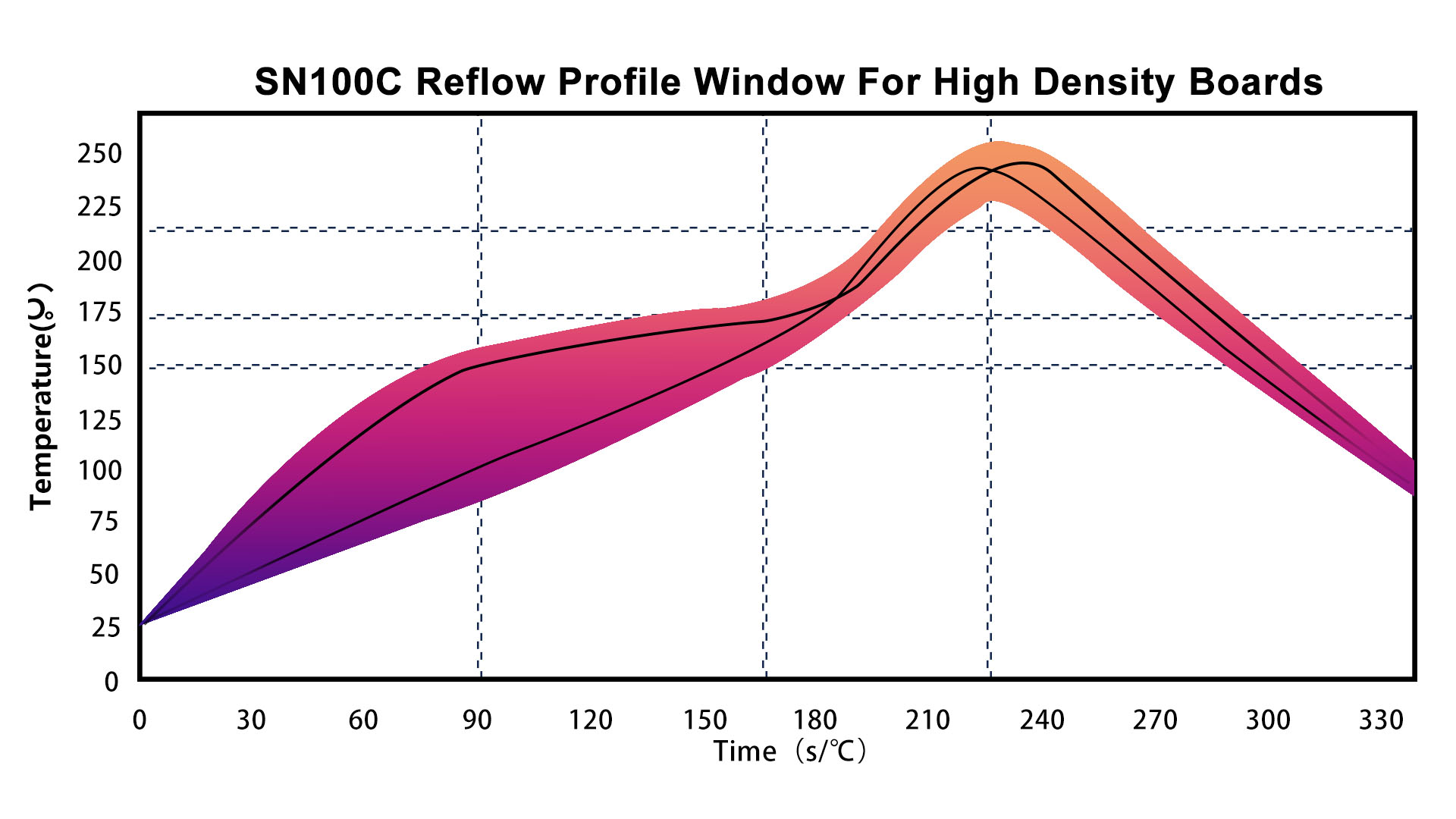
The formation of solder joints includes two processes - melting and recrystallization of the solder, and interfacial reaction. The interfacial reaction process can be divided into three segments: solder wetting (spreading), base metal melting/diffusion, and intermetallic compound (IMC) formation.
(1)The metallographic structure of Sn-37Pb alloy is determined by two metal phases - Sn with about 2% lead, Pb and about 20% tin solid solution. In a eutectic alloy, usually two metals behave as a uniform sheet-like structure of staggered laminates.
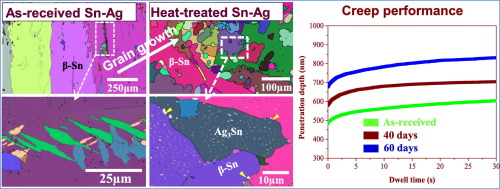
(2)The metallographic structure of Sn-3.5Ag alloy is "Sn+Ag3Sn". Generally, Ag3Sn can be uniformly dispersed in the parent Sn phase to form a cyclic structure, and the white particles are Ag3Sn, and the particle diameter is 1 μm or less.
(3)The metallographic structure of SAC alloy is pure Sn plus IMC (Cu3Sn, Ag3Sn), A is Sn phase, which is dendritic crystal structure; B is eutectic phase, including two-unit eutectic (Sn+Cu6Sn5, Sn+Ag3Sn And ternary eutectic (Sn+Cu6Sn5+Ag3Sn); C is an intermetallic compound (Cu6Sn5+Ag3Sn) at the grain boundary, and Ag3Sn is needle-like.
(4)Solder SAC305 with Sn-37Pb to form a metal-rich structure with more lead-rich phase than SAC.